Satisfying or unpleasant, poop is an essential part of the digestive process. Poop is primarily undigested protein, food, bacteria, salts, and other waste products released by the intestines.
Everyone’s poop may be unique in shape, size, and smell based on the food we eat, how much water we consume, and the illness we might have.
The normal human stool color is usually light to dark brown; however, it can be different if you consume beets or green vegetables.
A consistent change in stool color and texture should be evaluated as it may indicate an underlying problem, including tumors, celiac disease, ulcerative colitis, cancers, and many others.
It can be challenging to describe your poop. Hence doctors use an Nhs poo chart and stool color chart to ask about their Patient’s condition.
If you are one of those people who can’t figure out the science behind the normal poop and abnormal poop and want to know why it is essential to look closely at your poop, then continue reading to get answers to all your questions.
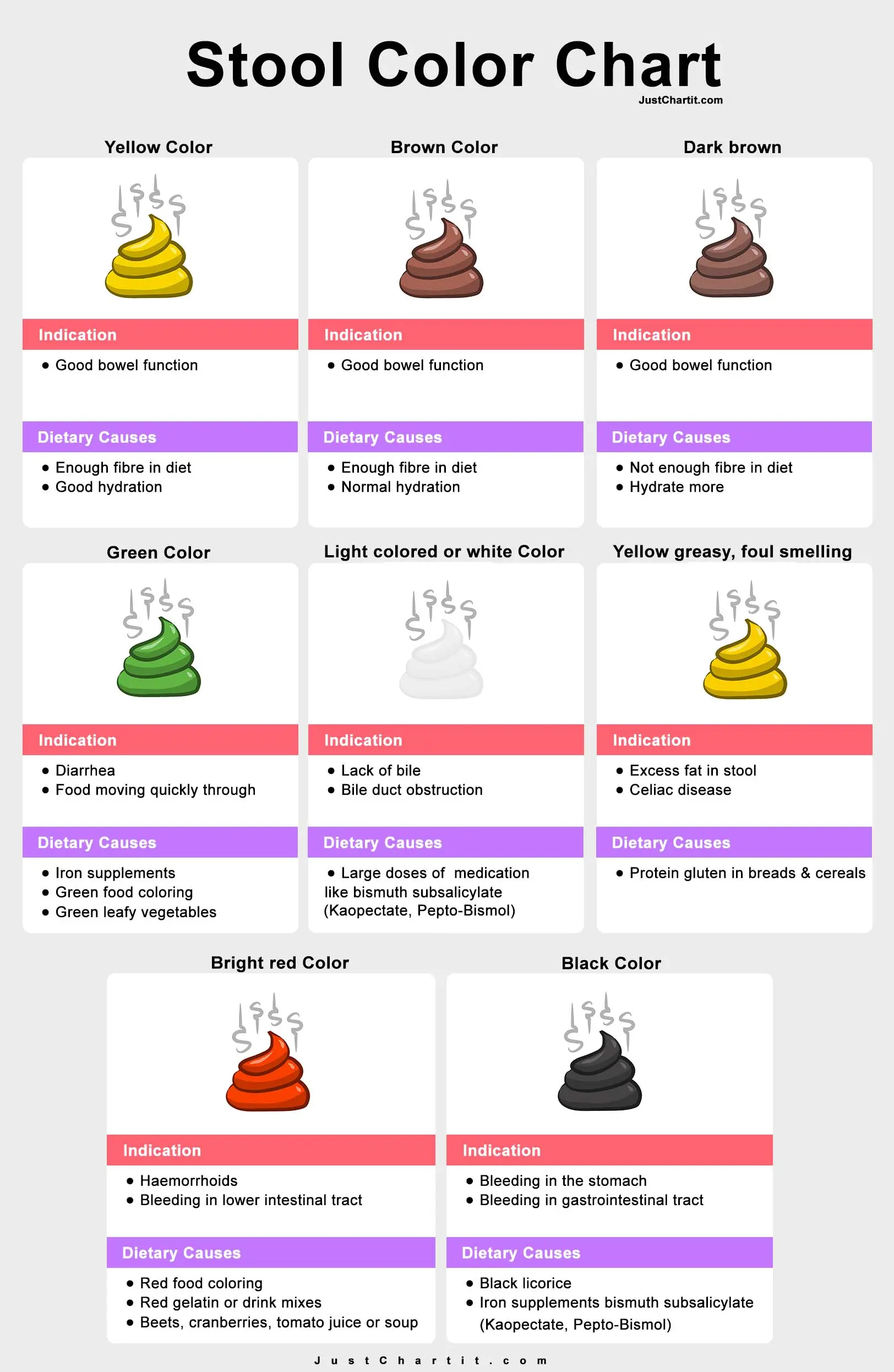
Stool Color Chart Meaning
| Poop Color | Poop Shape | Indication | Dietary Causes |
|---|---|---|---|
| Yellow | Sausage or snake shape | Good bowel function | Enough fiber in the diet, Good hydration |
| Brown | Sausage or snake shape | Good bowel function | Enough fiber in the diet, Normal hydration |
| Dark brown | Sausage shaped but lumpy | Good bowel function | Not enough fiber in the diet, Hydrate more |
| Green | Soft blobs to watery | Diarrhea, Food moving quickly through large intestine | Green leafy vegetables, Green food coloring, Iron supplements |
| Light colored or white | Soft blobs | Lack of bile, Bile duct obstruction | Large doses of medication like bismuth subsalicylate (Kaopectate, Pepto-Bismol) |
| Yellow greasy, foul smelling | Sausage or snake shape | Excess fat in stool, Celiac disease | Protein gluten in breads and cereals |
| Black | Sausage or snape shape to lumpy | Bleeding in the stomach, Bleeding in gastrointestinal tract | Black licorice, Iron supplements bismuth subsalicylate (Kaopectate, Pepto-Bismol) |
| Bright red | Lumpy to watery | Bleeding in lower intestinal tract, Haemorrhoids | Red food coloring, Beets, cranberries, tomato juice or soup, Red gelatin or drink mixes |
Light Yellow to Brown
Normal stool is brown because of the presence of bile in it. Standard stool color ranges from light yellow to brown with a soft texture. Any other color and texture may indicate an underlying problem, and you should visit a doctor.
Brown
Your stool depends on your diet and bile’s presence, which helps digest fats. Shades of brown are ok as they represent the colors of the food you consumed and the bitterness.
Green
Green stool may be caused by eating a lot of green vegetables. Overeating greens would mean that the food is moving through the system too quickly, and the bile doesn’t have time to do its magic resulting in diarrhea.
Light Colored
Light color poop could signify a lot of fat in it. This would mean that your body is having trouble absorbing fats. A white or chalky-looking stool can result from clogging of the bile duct or the effect of a medication.
Yellow, Greasy & Foul Smelling
A yellow but foul-smelling and greasy stool may result from fat in the stool. This can be caused by a pancreatic disease that prevents the delivery of enzymes to the intestines. A person having cystic fibrosis, chronic pancreatitis, or celiac disease may experience a similar stool color.
Black
Black stool may be caused by iron supplements or medicines that regulate stomach function. Black licorice can also cause a black stool color. However, if it smells bad and looks tarry, it may be a sign of bleeding in your digestive tract.
Bright Red
Consuming food with too much red coloring or red color medicine can result in red stool color. The bright red stool would indicate blood in the stool caused by bleeding in your large intestine or rectum from a hemorrhoid. If the stain persists, visit a doctor.
For more information on poop color meaning, look at the poop color chart above.
Types of Poop Chart
The consistency and shape of stool depend on how long it stays in the colon. The type of stool you are experiencing will help you analyze how well your digestive tract absorbs and processes the food you eat.
| Types | Stool Shape | Poop shape explained |
|---|---|---|
| Stool type 1 | Separate hard lumps | SEVERE CONSTIPATION |
| Stool type 2 | Lumpy and sausage like | MILD CONSTIPATION |
| Stool type 3 | A sausage shape with cracks in the surface | Normal |
| Stool type 4 | Like a smooth, soft sausage or snake | Normal |
| Stool type 5 | Soft blobs with clear-cut edges | LACKING FIBRE |
| Stool type 6 | Mushy consistency with ragged edges | MILD DIARRHEA |
| Stool type 7 | Liquid consistency with no solid pieces | SEVERE DIARRHEA |
What Causes Bristol Stool Type 1?
If you are experiencing small hard lumps or a sausage-shaped and lumpy stool, then you are experiencing type 1 stool. Is type 1 stool normal? This is a question that often haunts most people who experience it.
These stools are dry, complex, and may be painful to pass through, indicating that you are constipated. They are usually darker in color as they pass slowly through the digestive tract, and the water gets absorbed, making them dry and edgy.
How do you get rid of Type 1 poop is a question faced by most individuals as it’s a most common condition.
Try drinking more water, adding more fiber to your diet, performing physical activities regularly, or trying bowel training. However, if the problem persists, it’s best to visit a doctor and get proper medication.
Also read: Urine Color Chart
How Do You Fix Type 2 Poop?
Type 2 poop is sausage-shaped but lumpy and is hard to pass, just like type 1 poop. Type 2 poop is darker in color and indicates constipation. A low-fiber diet, inadequate fluids, and other gastrointestinal conditions cause type 2 poop.
Consuming a fiber-rich diet, drinking more fluids, trying bowel training, and performing regular physical activity are just a few ways to start with fic type 2 poop.
However, if you have a severe case of constipation, you may try over-the-counter laxatives that soften the stool and help the stool pass easily.
What Does Type 3 Stool Mean?
Type 3 stool is usually yellow to brown, sausage-like shape with cracks on its surface. Is it normal to poop 3? If you are among the people experiencing poop three, then you should be glad that your digestive system is working perfectly.
This also indicates that the digestive tract is efficiently breaking down food, absorbing nutrients, and releasing waste.
What Does Type 4 Stool Mean?
A sausage or snake-shaped stool that is easy to pass through is the characteristic of type 4 stool. One might wonder if a type 4 stool is healthy because of its shape. It is a healthy poop which indicates good digestive function and bowel movements.
What Does Type 5 Stool Mean?
If you are experiencing soft blobs down there, then it’s a sign of worry. This is a characteristic of type 5 stool that indicates a dietary problem and a borderline for diarrhea.
Some people may experience this type of stool daily, so they might need clarification on whether type 5 stool is normal. It may be expected for people with inadequate fiber in their diet or maybe consuming medicine that’s causing it.
It may be abnormal for others with an infection or a gastrointestinal condition that causes type 5 stool.
What Causes Bristol Stool Type 6?
Type 6 stool is mushy and has some blobs with ragged edges. If you have a similar experience and wonder, can type 6 poop be normal? What type 6 stool means is often a tricky question as there may be many causes behind this condition, but it’s a clear indication of diarrhea.
People often relate Type 6 stool with IBS because they have the same symptoms, such as bloating, cramps, and more. So does IBS cause type 6 stool? The answer is a little tricky.
If diarrhea is a symptom of IBS, you may experience more than three bowel movements daily. It’s best to immediately seek medical help for such a condition as the stool contains high water and mineral content that may cause severe dehydration in the body.
What Causes Bristol Stool Type 7?
Type 7 is a very loose or liquid form of stool that suggests diarrhea. They are also lighter in color as they pass through the digestive tract very quickly, so the bowel cannot absorb water.
People experiencing type 7 stool should increase their fluid intake and take medicines to prevent malnourishment and dehydration.
Stool Color For Babies
Infants’ poop color and consistency change during the first few weeks and months of their lives. As their diet changes, their poop color may vary from black to yellow and brown.
Breast milk and formula also affect the color of the baby’s stool. This can indicate a health issue if you notice red or white poop. Below, Learn about the different colors and causes behind baby poo color.
Newborn Poop Chart
| Poop Color | Representation |
|---|---|
| Black | Normal for babies one week or younger, May indicate internal bleeding in older babies |
| White | Sign of liver problem |
| Brown/Orange | Normal for formula-fed babies |
| Green | MedicationDiet |
| Red | Blood in stool |
| Yellow | Normal for breastfed babies |
FAQS
What color of stool should I be worried about?
The stool color may vary from brown to green; it’s normal. However, if you notice red or black stool, this may indicate blood; hence you should immediately consult a doctor.
Can probiotics change your stool?
Probiotics can change the stool’s color, but it affects the frequency of bowel movements more significantly. Probiotics are usually given to improve your gut health and regulate your pooping.
What is the color of diarrhea?
The green color is usually associated with diarrhea. When stool passes quickly through the digestive tract, there is little time for bilirubin to perform its chemical changes, which give the stool its natural color; hence the stool appears green
What are the symptoms of too many probiotics?
Bacteria in the probiotics are familiar to your body, but it is possible to experience side effects from taking probiotics in large amounts. You can feel bloating, nausea, gas, or diarrhea if you take probiotics in higher doses than recommended.
Conclusion
Sherry A. Rogers smartly explains why taking care of your digestive system is crucial: “The road to good health is paved with good intestines.”
If you are healthy and robust from the inside, you will experience standard stool color.
On the other hand, if you have digestive issues, hemorrhoids, cancers, or any other disease, your stool may change color to warn you of the upcoming trouble.
Therefore, it’s wise to look closely at your stool color and size to analyze your inner health. There’s no better way to do this than by consulting our stool color chart above.
