The term “fiber” describes a broad range of carbohydrates people cannot digest. Since we lack the enzymes needed to break them down, they move undamaged through most of the digestive tract.
So, fiber’s importance to your general health is not diminished because your body does not use it as fuel.
Fiber is quite beneficial. It exits your stomach undigested and travels to your colon, where it nourishes good gut flora.
As a result, it has several positive health effects. Also, some fibers may aid in fighting constipation, lowering blood sugar levels, and promoting weight loss.
You may already consume high-fiber foods daily. Or you could discover that some of your favorite foods offer enticing high-fiber food alternatives.
But how can you know if you consistently consume the advised 28 grams of fiber daily? You can estimate your daily fiber intake using this list of high-fiber foods.
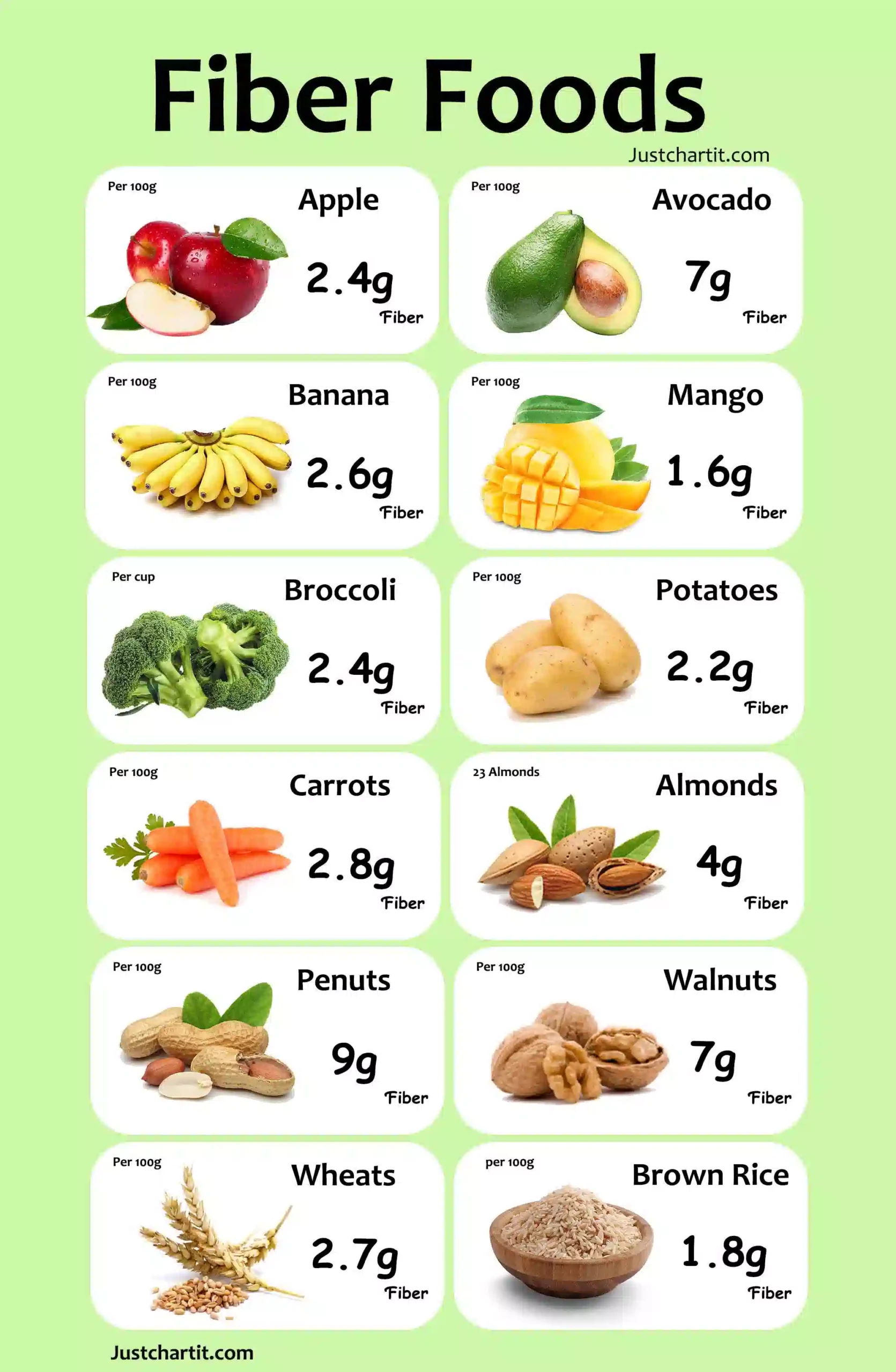
List of Vegetables that Contain Fiber
Fiber in Broccoli
A cruciferous vegetable rich in vitamins C and A is broccoli. Antioxidant polyphenols are also abundant in cruciferous vegetables. Raw broccoli has 2.6 g per 100 grams. You need roughly 9 cups of broccoli florets to get the recommended fiber.
Fiber in Carrots
Carrots are a good source of fiber whether you eat them raw or cooked, though just steaming them will help them release more beta carotene. Raw carrots contain 2.8 g of fiber per 100 grams, or 3.6 grams in 1 cup.
Fiber in Potatoes
One of the starchy vegetables used as a main dish is potatoes. They’re high in B vitamins, vitamin C, and magnesium. One large baked potato in its skin has 6.3 g of fiber.
List of Fruits that Contain Fiber
Fiber in Avocados
The creamy, rich flavor and beneficial fats of avocados are universally adored. Avocados contain vitamin C, E, potassium, magnesium, and several B vitamins.
Additionally, they offer many health advantages. A cup of raw avocado contains 10 grams of fiber or 6.7 g per 100 grams.
Fiber in Apple
Pectin is a form of soluble fiber that is abundant in apples. A medium-sized apple has 4.4 grams of fiber (2.4 g per 100 grams). It takes roughly seven apples to consume the daily recommended amount of fiber. That’ll take a long time to cut.
Fiber in Banana
It is one of the most malleable fruits and a persistent favorite. Nutrients such as vitamin C, B6, and potassium are abundant in bananas. Bananas have a filling power due to their high fiber content. A medium-sized banana has 3 grams of fiber or 2.6 g per 100 grams.
Fiber in Mango
Mangoes include soluble and insoluble fiber, which are equally crucial for healthy digestion. They also shield your body from various diseases.
In a 100-gram serving of mangoes, there is almost 1.6 g of fiber. This exotic fruit is one of the highest-fiber fruits available, containing roughly 5.4 grams of fiber per mango.
List of Nuts & Seeds that Contain Fiber
Fiber in Almonds
In addition to calcium, almonds are a good source of Protein, and vitamin E, which acts as an antioxidant. Almonds include 12.5 g of fiber per 100 grams. You need roughly 1 cup of almonds to get the required daily fiber.
Fiber in Peanuts
Peanuts are a great source of dietary fiber, numerous essential vitamins, and plant-based protein. One hundred grams of peanuts have 8.5 g of fiber. Around 1 cup of roasted, unsalted peanuts gives 28 grams of fiber.
Fiber in Walnuts
Walnuts are well-known for their omega-3 fats, which benefit the heart. It can also help you meet your fiber targets if you consume roughly 2 cups daily. They have 6.7 g of fiber per 100 grams.
List of Grains that Contain Fiber
Fiber in Wheat
Refined wheat has low fiber, while whole wheat is abundant in dietary fiber. It includes 12–15 percent of dietary fiber of its dry weight. One hundred grams of whole wheat grain has 13.1 g of fiber.
Fiber in Brown Rice
A nutrient-rich, high-fiber meal linked to a healthy diet is brown rice. This whole grain has vitamins, protein, and fiber and is a fantastic source of slow-release energy to maintain healthy bodily functions throughout the day. Brown rice has 3.5 grams of fiber per serving, or 1.8 grams per 100 grams.
How Much Fiber Do You Need?
According to the Academy of Nutrition and Dietetics, you should intake 14 grams of fiber for every 1,000 calories you consume daily. It equals about 24 grams of fiber for women, while for men, it equals about 38 grams.
Fortunately, boosting your fiber intake is relatively simple. Just include foods that are high in fiber in your diet.
Dietary Fiber Types
Fiber is often categorized as soluble or insoluble, depending on whether it dissolves in water.
- Soluble Fiber
This type of fiber turns into a gel-like substance when mixed into the water… It helps to lower blood sugar and cholesterol levels. Oats, peas, beans, apples, citrus fruits, carrots, barley, and psyllium are all sources of soluble fiber.
- Insoluble Fiber
Those who suffer from constipation may find that this sort of fiber helps move things through their digestive tract.
It adds bulk to the stool. Good sources of insoluble fiber include whole-wheat flour, nuts, beans, and vegetables, including cauliflower, green beans, and potatoes.
Benefits of Dietary Fiber
When consumed, dietary fiber can provide the following benefits.
- Protection Against Heart Disease
There has been extensive research on dietary fiber’s impact on heart health. Its role in avoiding cardiovascular disease and lowering blood pressure has been the primary concern.
According to a study, those with high fiber diets had a lower risk of heart disease and died from these ailments.
- Reducing Cholesterol
The presence of fiber in the digestive system can lessen the body’s absorption of cholesterol. Soluble fibers help lower blood cholesterol levels by lowering the amounts of low-density lipoprotein(bad cholesterol).
- Promoting a Healthy Weight
Fruits and vegetables, which are high in fiber, typically have fewer calories. Also, fiber helps decrease stomach digestion, which might prolong your feeling of fullness.
Researchers found in a 2019 study that those who consumed more dietary fiber lost weight. It also compelled them to adhere to their calorie-restricted diet.
- Adding Bulk to the Digestive Tract
Those who suffer from constipation or a slow digestive tract may benefit from increasing their fiber intake.
A 2015 review found that dietary fiber improves stool volume and encourages regular bowel movements. It also shortens the amount of time waste remains in the intestines.
- Promoting Blood Sugar Control
Your body could take longer to digest high-fiber foods. It makes it easier to maintain more stable blood sugar levels, which benefits those with diabetes.
- Reducing Gastrointestinal Cancer Risk
For a healthy digestive system, fiber is crucial. Consuming adequate fiber can help prevent some cancers, including colon cancer.
According to an analysis published in 2019, eating more fiber may lower one’s risk of colorectal cancer.
Fiber has many health advantages. It’s best to gradually add fiber-rich foods to your diet over a few days to prevent side effects like gas and bloating.
Increasing your fiber consumption while drinking lots of water may also help prevent these symptoms.
Summary
A healthy diet must contain dietary fiber—it lowers risks for cardiovascular disease, type 2 diabetes, and other malignancies. Fiber is essential for maintaining a healthy digestive system.
The majority of people do not consume enough fiber each day. People can enhance this measurement by consuming more high-fiber foods, fruits, and vegetables with the skins on.
