In recent generations, carbohydrates have been shaped by a variety of criticism. But, together with protein and fats, they are the essential nutrients the body requires.
Carbs are not only crucial for survival and healthy functioning but a successful diet. Below, you can see the high-carb vegetables chart. In this article, we will discuss the chunk of benefits that all these vegetables can provide.
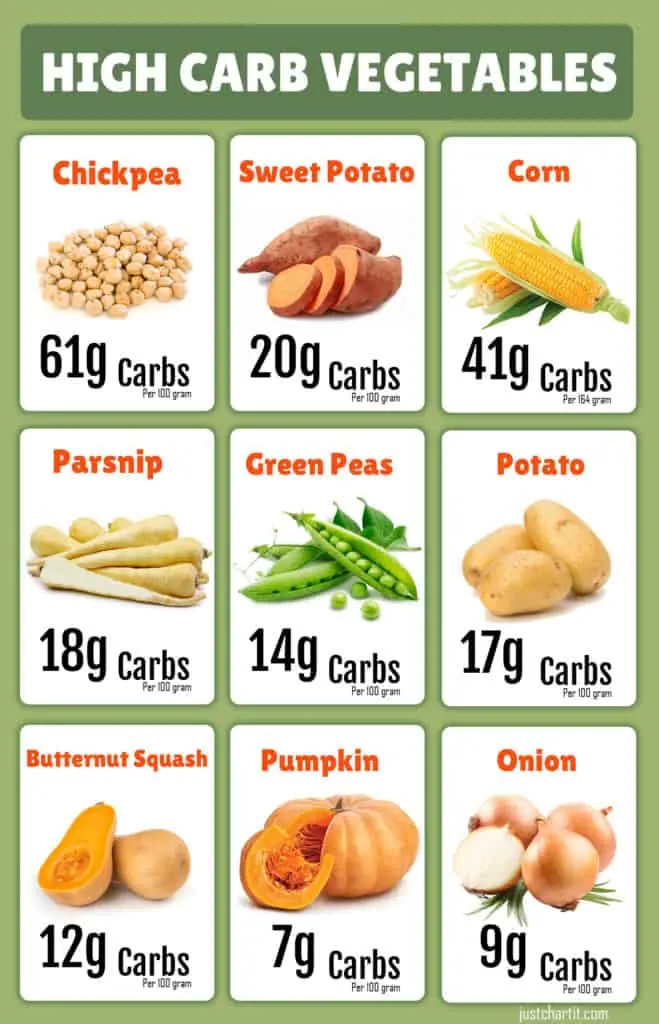
Let’s dive in deeper!
Carbs in Chickpeas
Chickpeas have the highest carbs count, as you can see in our high carbs vegetable chart. They effectively control your blood sugar using chickpeas.
The nutritional index of chickpeas is highly beneficial. That implies that your body absorbs it slowly and replenishes it.
They also have a kind of carbohydrate called amylase, which digests gradually. Both help prevents your insulin levels from rising too quickly. For those with diabetes, this would be excellent.
Note that if you are on a low-carb diet, take a few chickpeas on alternative days.
Carbs in Sweet Potato
A great choice with a wide variety of foods is sweet potatoes. There are 23,61 grams of carbohydrate in one medium sweet potato with the peel. Potassium and vitamins A & C are valuable sources of potatoes.
In a 2015 research, a few carbohydrate molecules in purple sweet potatoes might also benefit from fighting oxidants and cancer.
Also read: Leafy Vegetables list
Carbs in Corn
Corn is undoubtedly a delight for everybody. The health advantages of corn are several. It can support digestion due to its high fiber content and carbohydrates.
It also contains precious vitamins of B which are vital for your wellness. Corn offers essential Minerals like zinc, potassium, copper, iron, and magnesium to our body.
Carbs in Parsnip
Parsnips may appear like colorless carrots but are a root vegetable filled with a hint of spiciness and sweetness.
Along with high carbs, Parsnips are vitamin C boosters. A half parsnip can provide about vitamin C of around 17 milligrams, roughly 28% of the required daily dose.
Parsnips are also a good fiber source, with 3 to 5 g of fiber per serving overall. Threads are essential to a healthy intestine because they transport food through the digestive system and promote the health of the bowels.
Carbs in Green Peas
Believe me again if you think peas are low-lying, regular veggies! These little beaded gems provide a powerful punch as far as the nutrients and health advantages are concerned.
Its calorie count is relatively modest, at 170 gram calories per 1/2 cup serving. Roughly 70% of these calories are carbohydrates, while the remaining are protein and a tiny bit of fat.
Green peas’ beneficial carbohydrates and protein composition make them an excellent alternative for individuals who do not consume meat.
The probability of inflammation disorders such as diabetes, cardiovascular diseases, and arthritis has been reduced by anti-inflammatory elements in peas.
Carbs in Potatoes
Potatoes are famous carbohydrates that supply many nutritious vitamins, proteins, and chemicals for us.
Some vitamins and minerals are decreased in potatoes throughout the cooking process, and that’s they are thought to be a bad snack, but baking or skin-boiling might lessen this decrease.
Potassium is mainly stored in the skin of potatoes and can help cardiac health. Moreover, potatoes relatively give a complete stomach feel. This is the reason they may be beneficial as part of a loss of weight diet.
Carbs in Butternut Squash
It offers a remarkable variety of nutrients with little over 80 calories, 12g of carbs, and 4 g of sugar in one cup.
The flesh in the squash is a perfect offering filled with beta carotene transformed into vitamin A by the body system.
For seeing and several other biological processes, beta carotene is needed. A portion of squash also includes more potassium, which assists blood pressure to be regulated.
Carbs in Pumpkin
Pumpkin is a lower-carb fruit than most other vegetables in our chart. Pumpkin has less sugar and carbohydrate compared to other starchy vegetables such as maize and potatoes.
Pumpkins are good as they’re a high-vitamin A and fiber antioxidant. These qualities are beneficial for any diet since they assist in reducing weight. The fruit is rich in fiber. Therefore the net carbohydrates are minimal.
Carbs in Onion
Onions are healthy and are daily meal partners. Although they are relatively rich in carbohydrates, their strong flavor often consumes them in tiny quantities.
Half a cup of raw sliced onions (58 grams), containing 6 g of carbohydrates, including fiber. Onions are rich in quercetin antioxidants, which can reduce blood pressure.
One research in overweight and obese individuals with PCOS revealed that red onion intake decreased LDL cholesterol levels.
